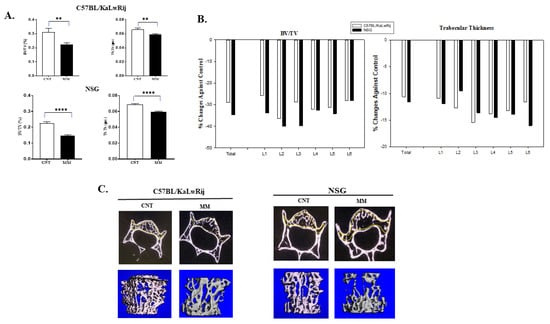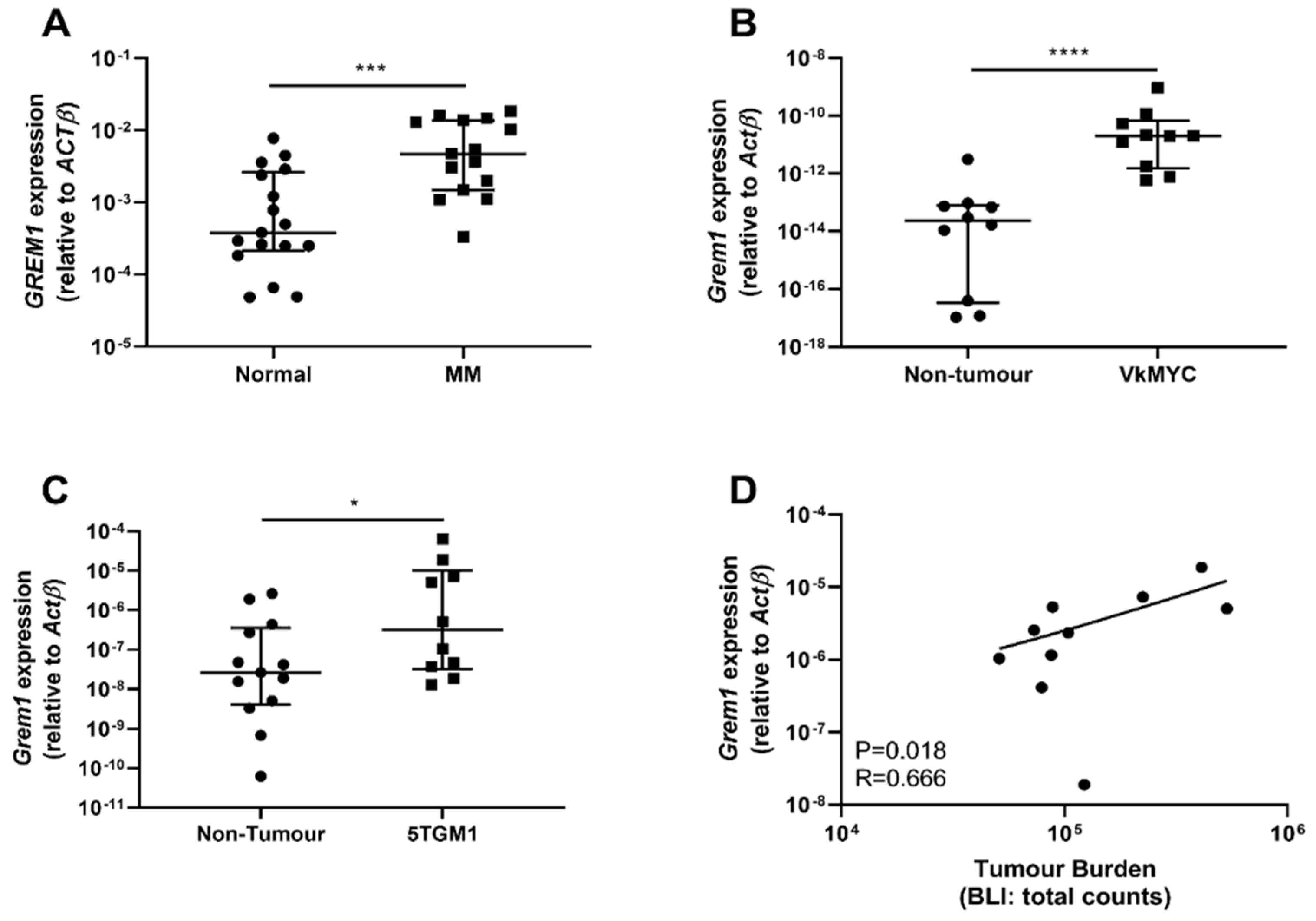
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Targeted Disruption of Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Derived Gremlin1 Limits Multiple Myeloma Disease Progression In Vivo
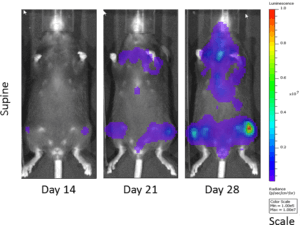
Visualization of 5T33 myeloma cells in the C57BL/KaLwRij mouse: Establishment of a new syngeneic murine model of multiple myelom
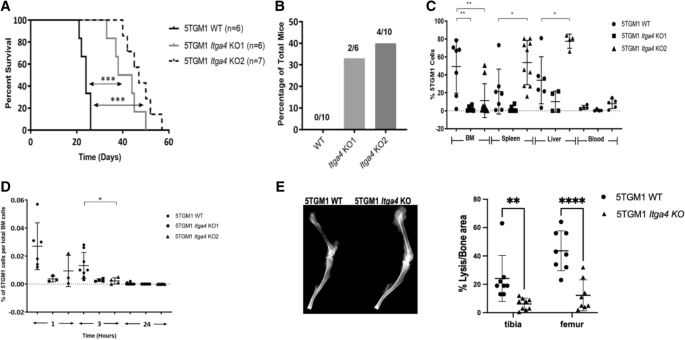
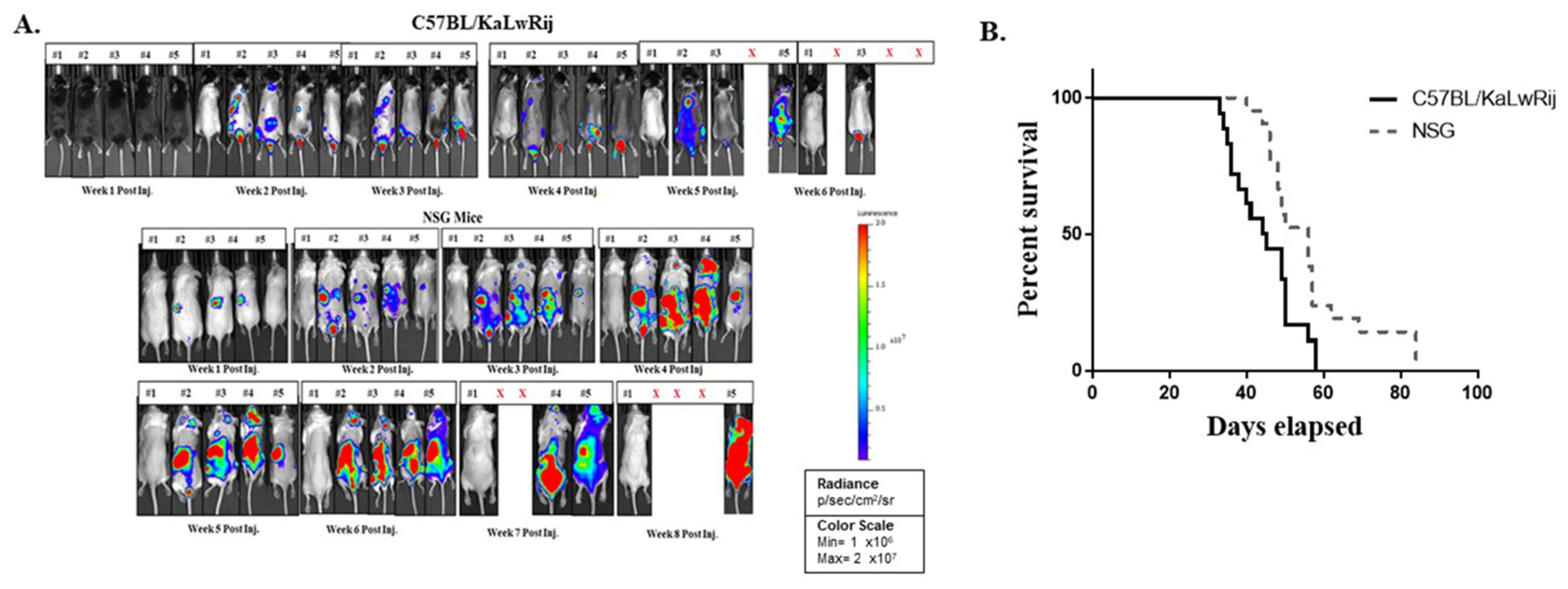
Ablation of VLA4 in multiple myeloma cells redirects tumor spread and prolongs survival | Scientific Reports
Myeloma plasma cells alter the bone marrow microenvironment by stimulating the proliferation of mesenchymal stromal cells | Haematologica

Visualization of 5T33 myeloma cells in the C57BL/KaLwRij mouse: establishment of a new syngeneic murine model of multiple myeloma - ScienceDirect

In vivo effect of lenalidomide in myeloma-bearing mice. C57BL/KaLwRij... | Download Scientific Diagram

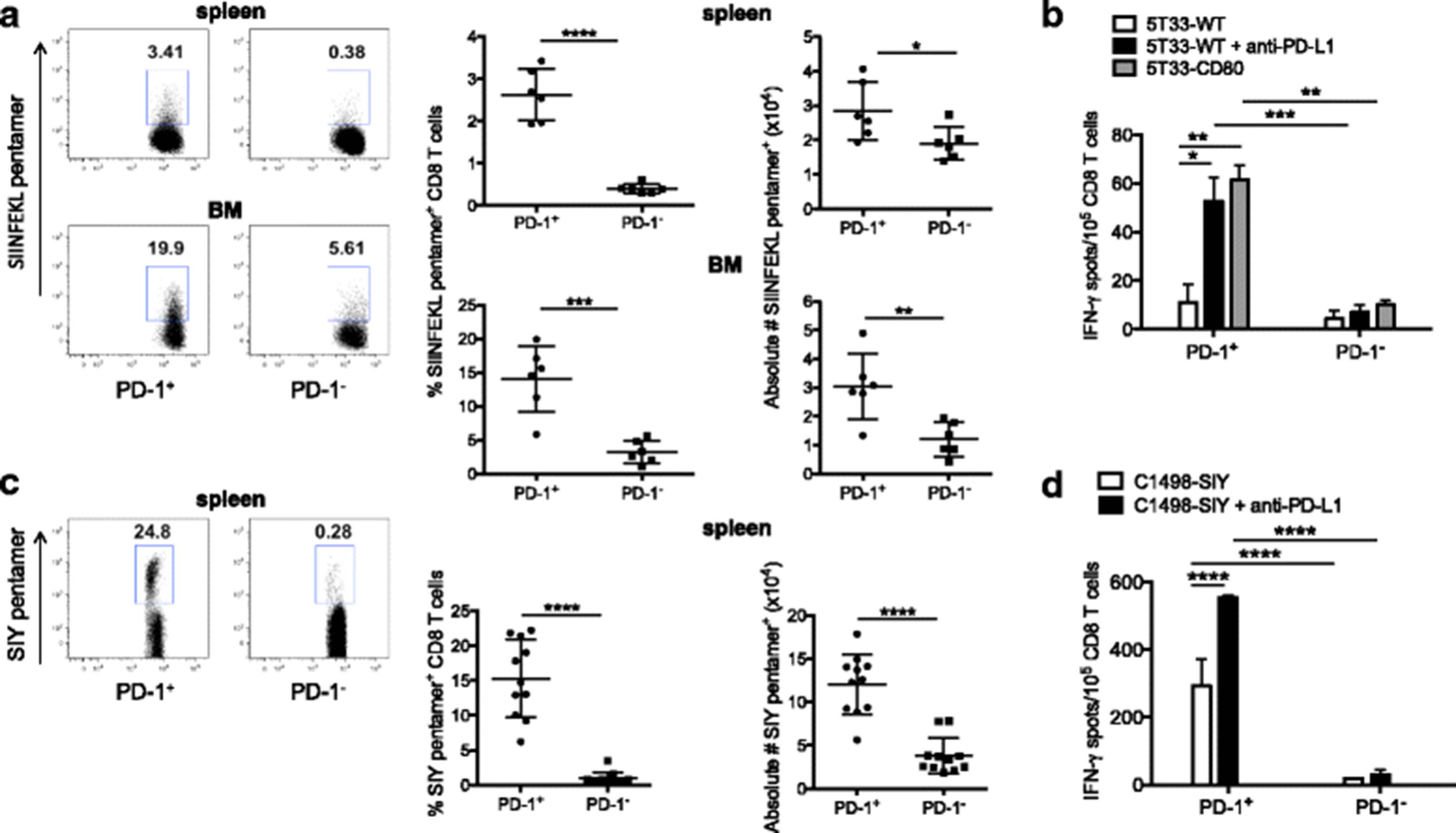
Characterization of the role of Samsn1 loss in multiple myeloma development - Friend - 2020 - FASEB BioAdvances - Wiley Online Library

Characterization of the role of Samsn1 loss in multiple myeloma development - Friend - 2020 - FASEB BioAdvances - Wiley Online Library
Whole Genome Sequence of Multiple Myeloma-Prone C57BL/KaLwRij Mouse Strain Suggests the Origin of Disease Involves Multiple Cell Types | PLOS ONE
Tenfold Increased Incidence of Spontaneous Multiple Myeloma in Long-Term Immunosuppressed Aging C57BL/KaLwRij Mice
Follow-up of bone lesions in an experimental multiple myeloma mouse model: description of an in vivo technique using radiography
Whole Genome Sequence of Multiple Myeloma-Prone C57BL/KaLwRij Mouse Strain Suggests the Origin of Disease Involves Multiple Cell Types | PLOS ONE

Erythropoietin induces tumor regression and antitumor immune responses in murine myeloma models | PNAS

Chronic intermittent hypoxia enhances disease progression in myeloma-resistant mice | American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology
Whole Genome Sequence of Multiple Myeloma-Prone C57BL/KaLwRij Mouse Strain Suggests the Origin of Disease Involves Multiple Cell Types | PLOS ONE
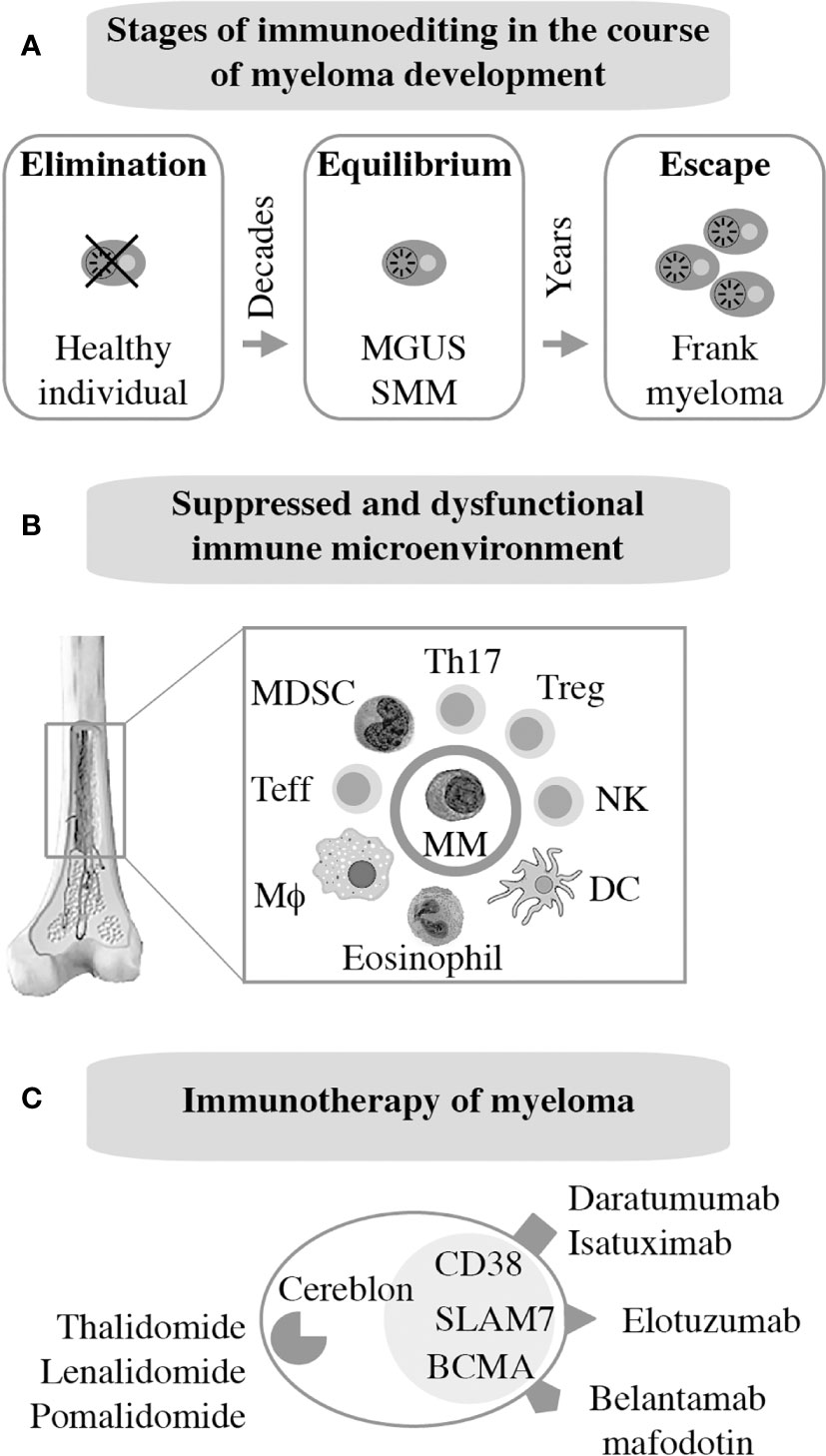
Frontiers | Laboratory Mice – A Driving Force in Immunopathology and Immunotherapy Studies of Human Multiple Myeloma

CD4⁺ T cells play a crucial role for lenalidomide in vivo anti-tumor activity in murine multiple myeloma. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Whole Genome Sequence of Multiple Myeloma-Prone C57BL/KaLwRij Mouse Strain Suggests the Origin of Disease Involves Multiple Cell Types | PLOS ONE
Myeloma plasma cells alter the bone marrow microenvironment by stimulating the proliferation of mesenchymal stromal cells | Haematologica